Tomorrow is the start of the new financial year and as always, there are changes to the super system. Here are five important changes that come into effect on 1 July.
1. Employers will now contribute 10.5% to super
The rate of employer contributions to super (the so-called ‘super guarantee levy’) is increasing from 10.0% to 10.5%. If you earn $100,000, your employer will now contribute $10,500 rather than $10,000 to your super fund.
Super is payable on salary and wages, including bonuses, but not overtime. Technically, it is not payable on amounts in excess of a salary of $240,880 ($60,220 per quarter) although many employers choose to pay it.
There is no change to the concessional contributions cap of $27,500. Concessional contributions are the employer’s 10.5% plus any amount you choose to salary sacrifice, plus any amount you contribute and claim a tax deduction for. If you are at risk of going over the cap of $27,500, talk to your employer – there is no upside in being over the cap.
Another change that will impact some employers and casual staff is the abolition of the rule that exempted employers from paying super if the employee’s gross wage was less than $450 in any month. From 1 July, all casual staff will be entitled to super.
2. 67 to 74-year-olds can make big ‘one-off’ contributions to super
A big change to the super rules this year is the abolition of the ‘work test’ for those aged 67 to 74 years. From 1 July, anyone in this age bracket can access the concessional contributions cap of $27,500 and the non-concessional contributions cap of $110,000.
Personal (non-concessional) contributions of up to $110,000 are allowed provided your total superannuation balance is less than $1.7 million at the start of the year, irrespective of work status. Importantly, those aged 67 to 74 years can now access the ‘bring-forward’ rule, which allows them to make 3 years’ worth of non-concessional contributions in one hit. Potentially, an individual could get $330,000 into super in one hit and a couple, $660,000.
There is one important caveat to accessing the ‘bring-forward’ rule, your total superannuation balance. If it is between $1.48 million and $1.59 million, the maximum amount you can contribute is $220,000. If it is between $1.59 million and $1.7 million, the maximum amount is $110,000 and if over $1.7 million, no contribution is allowed.
Salary sacrifice contributions are allowed irrespective of work status. Those aged 67 to 74 years who are seeking to claim a tax deduction for a personal super contribution will still need to satisfy the ‘work test’.
3. Downsizer contribution age threshold reduces to 60
“Downsizers” who are aged 60 or older can make a special contribution of up to $300,000 into their super. From 1 July, the age threshold reduces from 65 years to 60 years. Downsizer contributions are not subject to the contribution caps and can be made irrespective of your total superannuation balance.
To qualify, you need to have owned your home for 10 or more years prior to the sale. You need to make the contribution within 90 days of receiving the proceeds of the sale, and you can’t previously have made a downsizer contribution. Couples can potentially make a contribution of $300,000 each.
If you are in the pension phase of super, downsizer contributions will count against the transfer balance cap of $1.7 million.
4. First home super saver limits are being increased
A “no brainer” savings scheme for those looking to buy their first home, the limit on how much you can access from super to help fund the purchase of a home is being increased from $30,000 to $50,000.
The amount you contribute to super to count as part of this scheme is capped at $15,000 pa. Contributions take the form of pre-tax salary sacrifice (concessional contributions) or post-tax personal contributions (non-concessional). Your employer’s 10.5% doesn’t count.
The first home super saver scheme delivers a high, secure return for aspiring homebuyers, much higher than if investing in a term deposit. For more information, visit: https://www.ato.gov.au/Individuals/Super/Withdrawing-and-using-your-super/First-Home-Super-Saver-Scheme/
5. Reduced minimum pension payments
The Government has extended for another year a measure introduced during the Covid-19 pandemic that halves the minimum amount retirees must take as a super pension.
The minimum pension payment is age-based and calculated on the balance of your super assets in the pension phase at the start of the financial year (1 July). The factors to apply in 22/23 are shown below:
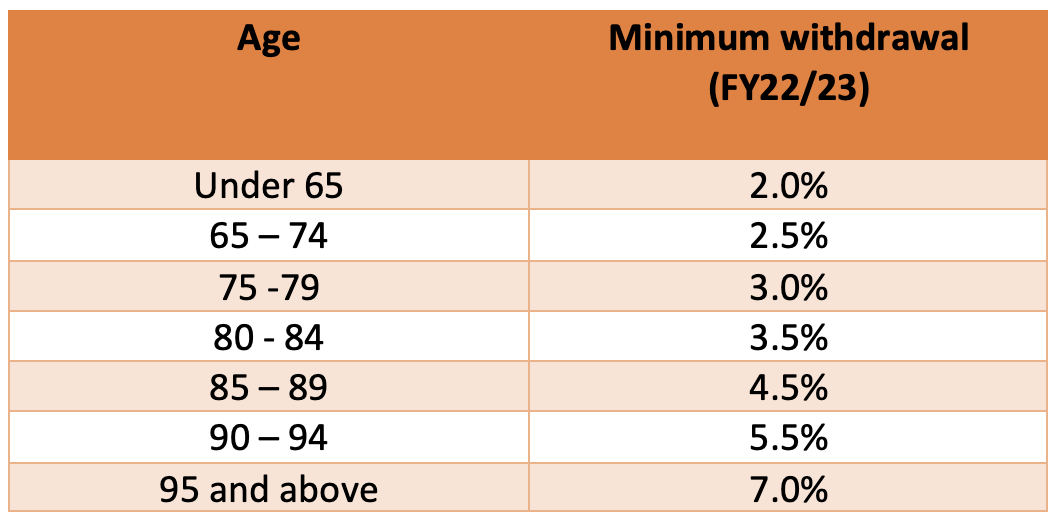
For example, if you were aged 66 on 1 July 2022 and had an account balance of $1,000,000, your minimum payment is 2.5% of $1,000,000 or $25,000. You can take your pension at any time and in any amount(s), but your aggregate drawdown over the year must exceed the minimum amount. If you commence a pension mid-year, the minimum amount is pro-rated according to the number of days remaining until the end of the financial year.
Important: This content has been prepared without taking account of the objectives, financial situation or needs of any particular individual. It does not constitute formal advice. Consider the appropriateness of the information in regards to your circumstances.

